What’s new in ISO 27001?

Did you know that every day, a number of security incidents are uncovered that are publicly disclosed and lead to data compromise? We hear about data breaches and other cybercrimes in the news every day, and the risks of security and privacy breaches are surging as people rely more and more on the internet. We are all aware that a significant amount of data is shared online virtually daily and that many organizations need a considerable amount of our personal information to run their various operations. There is no doubt that this data is the most valuable asset on its own for businesses of all sizes and orientations nowadays.
However, many malicious actors threaten the security and privacy of this valuable data, and thus businesses are immediately exposed to various data security and privacy risks.
Given how damaging these data breaches or other cybercrimes can be for the impacted businesses, as well as for their employees, customers, and other relevant persons whose sensitive data may have been compromised, shouldn’t it be a top concern for organizations? Answer is a definite YES! Therefore, protecting the security and privacy of this crucial, sensitive and confidential data and information needs to be a key concern for businesses because failing to do so will result in severe consequences. Organizations can be kept secure by adopting, establishing, implementing and maintaining the ISO/IEC 27000 set of standards.
The ISO/IEC 27001 standard, which governs information security management and safeguards the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of businesses’ information assets, has just been upgraded to address current cybersecurity risks and foster trust. So in this article, we will discuss what has been updated in the ISO/IEC 27001 standard.
What is ISO 27001?
Let us first describe the ISO/IEC 27001 standard, often known as the ISO 27001 standard, before proceeding to the most recent updates. ISO 27001 is an international management systems standard explicitly created to protect information, provide robust Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) requirements, and maintain information in its original form. It is the most well-known standard in the world for ISMS and its specifications.
ISO 27001 benefits:
Implementing ISO 27001 demonstrates to stakeholders and customers that a business is committed to securely and safely managing information, which fosters confidence in those entities.
What’s new in ISO 27001?

The ISO/IEC 27001:2022 (ISO/IEC 27001:2022-Information Security, Cybersecurity, and Privacy Protection) standard has undergone several significant and minor modifications. We will provide an overview of the standard modifications.
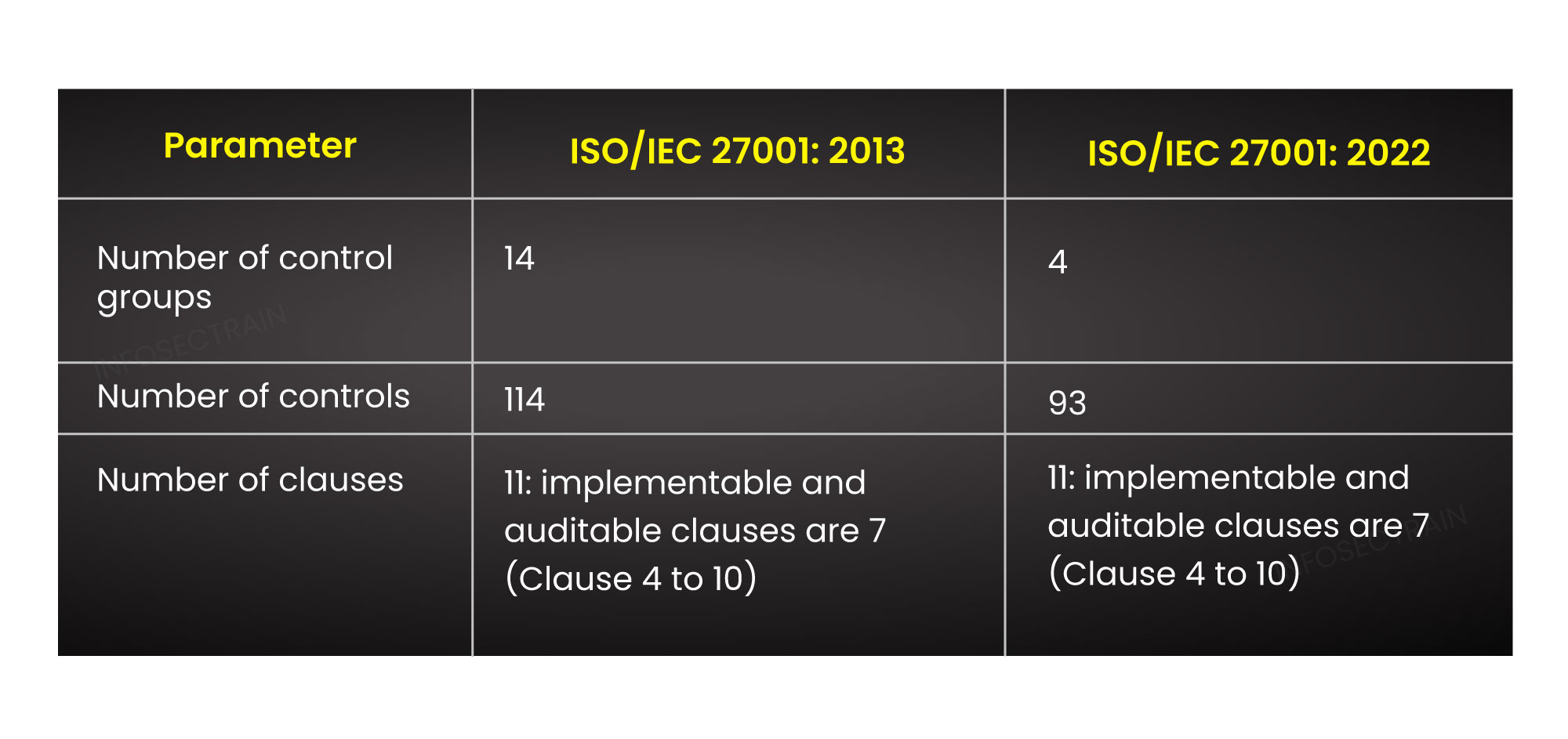
1. In Annex A, the number of controls and their divisions have changed in a variety of ways:
Annex A of ISO 27001 contains one of the main modifications in ISO/IEC 27001:2022. In ISO/IEC 27001:2013, there were 114 controls in total across the 14 control areas or sections. On the other hand, ISO/IEC 27001: 2022 is more in line with the more recent ISO 27002 standard. As per the restructuring, all the controls have now been divided into 4 categories/ control areas or sections. The controls have been lowered from 114 to 93, including restructuring of earlier controls and introduction of new controls in the new ISO 27001 standard. These controls are divided into these four control areas based on five different attribute types. Below is the bifurcation of these updates.
a) The control groups have been reduced to 4 from 14
- A.5 Organizational controls: (37 controls)
- A.6 People controls: (8 controls)
- A.7 Physical controls: (14 controls)
- A.8 Technological controls: (34 controls)
b) The number of controls has been reduced to 93 from 114
- New controls added: 11
- Unmodified controls: 5
- Renamed controls: 23
- Merged controls: 57 into 24
- Divided controls: 1 into 2
c) These 93 controls have been restructured into the four control groups or sections mentioned above.
d) The following new controls have been added to these control groups:
- A.5.7 Threat intelligence
- A.5.23 Information security for the use of cloud services
- A.5.30 ICT readiness for business continuity
- A.7.4 Physical security monitoring
- A.8.9 Configuration management
- A.8.10 Information deletion
- A.8.11 Data masking
- A.8.12 Data leakage prevention
- A.8.16 Monitoring activities
- A.8.23 Web filtering
- A.8.28 Secure coding
e) The five attributes are:
- Control type
- Information security properties
- Cybersecurity concepts
- Operational capabilities
- Security domains
2. Clauses 4 to 10 have undergone minor changes:
There are further minor changes to the clause sections of the new versions of the ISO/IEC 27001:2022 standard.
- Clause 4: Context of the organization
When organizations understand and are aware of the demands and expectations of interested parties, they must now decide which of these needs will be addressed by the ISMS. - Clause 5: Leadership
It contains specific requirements that the organization is made aware of the responsibilities and authority associated with information security roles. - Clause 6: Planning
The information security objectives must be monitored and documented in writing using a well-structured format. - Clause 7: Support
A requirement to define “how to communicate” has taken the place of requirements to describe who will communicate and the procedures for effective communication. - Clause 8: Operation
Instead of only processes, organizations must now maintain control over and document “externally offered processes, products, or services”, that are important to the ISMS and are provided as anticipated. - Clause 9: Performance evaluation
The organization must also assess the performance of information security and the efficiency of the ISMS. - Clause 10: Improvement
One of the significant adjustments made to the new ISO 27001:2022 is the adaptation of the current structure to the Harmonized Structure with a focus on the Continuous Improvement Process (CIP). Presently, the handling of nonconformities and corrective actions in retrospect comes before the element of prospective continuous development.
How does an organization get ISO 27001 certification?
An organization must contact a different third-party certifying body whose auditors will come and check all the controls to see if they are in place or not if it believes that all 93 controls are in place and have been applied in the organization. After auditing, they will issue ISO 27001 certification if they assess that all controls are in place.
About Azpirantz Technologies LLP
If any organization is planning to get the new ISO 27001: 2022 certification or wants to upgrade its existing credential to the latest version, Azpirantz can guide you in the transition. The mission of Azpirantz Technologies LLP, also known as Azpirantz, is to enable its clients to focus on their core businesses by analyzing the evolving cybersecurity threat landscape, taking care of their cybersecurity and compliance through top-notch services, and offering them effective techniques.
We at Azpirantz have cybersecurity consultants and professionals who are highly skilled in cutting-edge technology and can provide our customers with high-quality services. Thus, we strive to offer our customers a seamless experience to combat evolving cybersecurity threats.
Recommended Posts
-

Tips to Maintain ISO 27001 Certification
Feb 20, 2023 -

What is ISO 27001 certification?
Jan 2, 2023